Want to hire Hyperledger developer? Then you should know!
Hyperledger is an open-source collaborative effort, hosted by the Linux Foundation, focused on developing enterprise-grade blockchain technologies. It provides frameworks, tools, and libraries for building permissioned blockchain systems, and is not designed to be a cryptocurrency itself. Hyperledger aims to facilitate cross-industry collaboration and standardization in the development of blockchain solutions for various sectors.

Pros & cons of Hyperledger
7 Pros of Hyperledger
- Increased Transparency: Hyperledger provides a transparent and immutable record of transactions, making it easier to track and verify data.
- Enhanced Security: With advanced cryptographic techniques and permissioned access, Hyperledger ensures a high level of security for sensitive data.
- Cost Efficiency: Hyperledger eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing costs associated with third-party services and minimizing transaction fees.
- Improved Efficiency: The distributed ledger technology of Hyperledger enables streamlined and automated processes, eliminating manual tasks and reducing the chances of errors.
- Flexible Governance Models: Hyperledger allows organizations to choose their own governance models, enabling them to tailor the framework to their specific needs and requirements.
- Interoperability: Hyperledger supports interoperability with existing systems, enabling seamless integration with legacy infrastructure and facilitating collaboration between different organizations.
- Community Support: Hyperledger benefits from a large and active community of developers and contributors, providing ongoing support and driving innovation in the ecosystem.
7 Cons of Hyperledger
- Complexity: Implementing and managing a Hyperledger network can be complex, requiring expertise and resources to ensure proper configuration and maintenance.
- Limited Scalability: Hyperledger may face scalability challenges when dealing with a high volume of transactions, which can affect its performance in certain use cases.
- Limited Privacy: While Hyperledger offers privacy controls, the level of privacy may not be as robust as some other blockchain solutions, potentially posing challenges for certain industries with stricter privacy requirements.
- Dependency on Consensus: Hyperledger relies on consensus mechanisms, which can slow down transaction processing and decision-making in certain scenarios.
- Regulatory Challenges: The evolving regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain and cryptocurrencies can pose challenges for organizations utilizing Hyperledger, requiring them to navigate complex legal frameworks.
- Technical Expertise: Implementing and maintaining a Hyperledger network requires technical expertise, which may be a barrier for organizations lacking the necessary skills or resources.
- Dependency on Trust: Hyperledger’s permissioned network model relies on trust among network participants, which may not be suitable for scenarios where complete decentralization and trustlessness are desired.
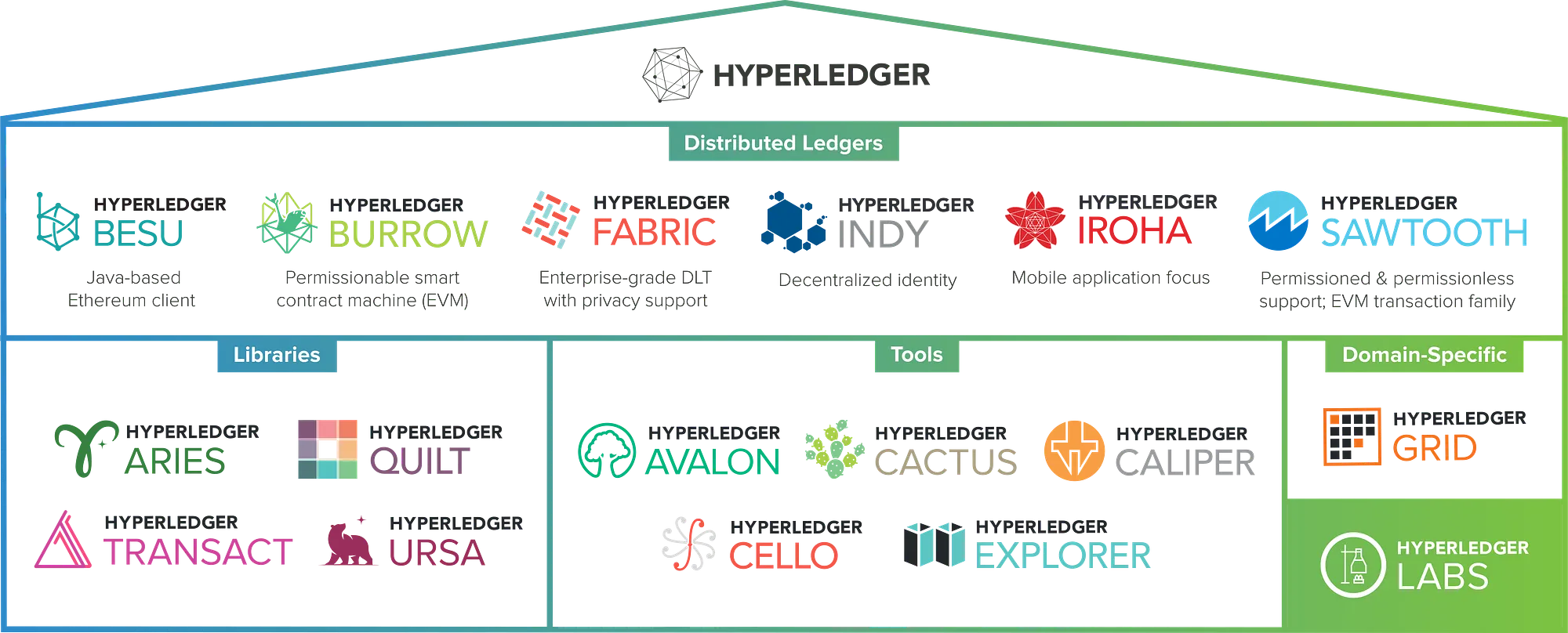
TOP 10 Hyperledger Related Technologies
Programming Languages
Hyperledger supports various programming languages including JavaScript, Java, Go, and TypeScript. JavaScript is widely used for developing web-based applications, while Java provides scalability and robustness. Go is known for its simplicity and efficiency, making it suitable for building distributed systems. TypeScript offers type safety and enhanced tooling for larger projects.Hyperledger Fabric
Fabric is one of the most popular frameworks within the Hyperledger ecosystem. It provides a modular architecture that allows for the customization of components, consensus protocols, and smart contract execution engines. Fabric supports distributed ledger technology and enables the creation of permissioned blockchain networks.Hyperledger Composer
Composer is a development toolset for building blockchain applications on top of Hyperledger Fabric. It simplifies the process of creating smart contracts and defining business network models. With Composer, developers can rapidly prototype and deploy blockchain solutions without deep knowledge of the underlying technology.Hyperledger Indy
Indy is a decentralized identity platform designed specifically for self-sovereign identity. It enables individuals to have full control over their digital identities and provides a secure and interoperable infrastructure for identity management. Indy is particularly relevant for applications that require privacy and trust in identity verification.Hyperledger Sawtooth
Sawtooth is another prominent framework within Hyperledger. It focuses on scalability and modularity, making it suitable for enterprise-grade applications. Sawtooth utilizes a unique consensus algorithm called Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET) and supports parallel transaction execution, allowing for high-performance blockchain networks.Hyperledger Burrow
Burrow is an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatible execution engine within Hyperledger. It allows developers to write smart contracts using Solidity, the same language used in Ethereum, while benefiting from the enterprise features provided by Hyperledger. Burrow ensures compatibility with existing Ethereum tooling and infrastructure.Hyperledger Caliper
Caliper is a benchmarking tool for measuring the performance of blockchain solutions built on Hyperledger. It allows developers to simulate various workloads and evaluate the scalability and efficiency of their applications. Caliper helps identify potential bottlenecks and optimize the performance of Hyperledger-based systems.
TOP 10 Facts about Hyperledger
- Hyperledger is an open-source project and collaboration hosted by the Linux Foundation that aims to advance cross-industry blockchain technologies.
- It was launched in December 2015, and since then, it has gained significant traction and support from various industries including finance, healthcare, supply chain, and more.
- Hyperledger offers a modular framework for developing blockchain-based applications and platforms, allowing organizations to build and deploy distributed ledgers tailored to their specific needs.
- One of the key features of Hyperledger is its focus on privacy and confidentiality, enabling enterprises to control access to sensitive information within their blockchain networks.
- Hyperledger Fabric is one of the widely used frameworks within the Hyperledger ecosystem. It provides a scalable and flexible foundation for building permissioned blockchain networks.
- Unlike public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum, Hyperledger networks are permissioned, meaning that participants must be authenticated and authorized to join the network.
- Hyperledger Sawtooth is another popular framework that emphasizes modularity and scalability. It enables developers to create and manage distributed ledger applications with ease.
- Hyperledger supports a wide range of programming languages, including Go, Java, JavaScript, and Python, making it accessible to developers with diverse backgrounds and skill sets.
- Several prominent companies and organizations, including IBM, Intel, and JPMorgan Chase, are active contributors to the Hyperledger project, further validating its industry relevance.
- Hyperledger is continuously evolving and improving, with regular updates, releases, and collaboration among its vibrant community of developers, researchers, and industry leaders.
How and where is Hyperledger used?
| Case Name | Case Description |
|---|---|
| Supply Chain Management | Hyperledger can be used to create a transparent and efficient supply chain management system. It allows all participants in the supply chain to securely record and track the movement of goods, reducing fraud and improving traceability. |
| Healthcare Data Management | Hyperledger can help in managing healthcare data securely and efficiently. It enables the creation of a decentralized electronic health record system, ensuring that patient data is stored securely and can be accessed by authorized parties in a controlled manner. |
| Identity Management | Hyperledger can be utilized to develop robust identity management systems. It allows for the creation of decentralized identity systems where users have control over their personal information, reducing the risk of identity theft and providing a more secure authentication process. |
| Financial Services | Hyperledger can revolutionize the financial services industry by providing a secure and transparent platform for conducting transactions. It enables the development of decentralized payment systems, smart contracts, and digital asset management, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. |
| Real Estate Transactions | Hyperledger can streamline the real estate transaction process by providing a transparent and immutable ledger for recording property ownership and transfers. It eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing the speed of transactions. |
| Insurance Claims Processing | Hyperledger can automate and streamline insurance claims processing, reducing fraud and improving the efficiency of the process. It enables the creation of a decentralized system where claims can be verified and processed in a transparent and secure manner. |
| Energy Trading | Hyperledger can facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading by creating a decentralized marketplace for buying and selling energy. It allows for the direct exchange of energy between producers and consumers, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing costs. |
| Intellectual Property Management | Hyperledger can be used to create a secure platform for managing intellectual property rights. It enables the recording and tracking of ownership and licensing agreements, ensuring that creators’ rights are protected and providing a transparent system for resolving disputes. |
| Voting Systems | Hyperledger can enhance the integrity and transparency of voting systems by providing a secure and auditable platform for conducting elections. It enables the creation of decentralized voting systems, ensuring that votes are recorded accurately and can be verified by stakeholders. |
Talk to Our Expert
Our journey starts with a 30-min discovery call to explore your project challenges, technical needs and team diversity.

Yaroslav Kuntsevych
co-CEO
