Want to hire XSLT developer?
Introduction
XSLT, or Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations, emerged in 1998 as a method to manipulate XML data—a task still relevant in 2025. It reshapes XML into formats like HTML or plain text, a specialized craft. This page examines the role of XSLT developers, their technical demands, and their place in modern systems. At Upstaff, we maintain a team of such experts—seasoned, not borrowed—ready to tackle XML challenges. We match them to your needs, no fumbling required.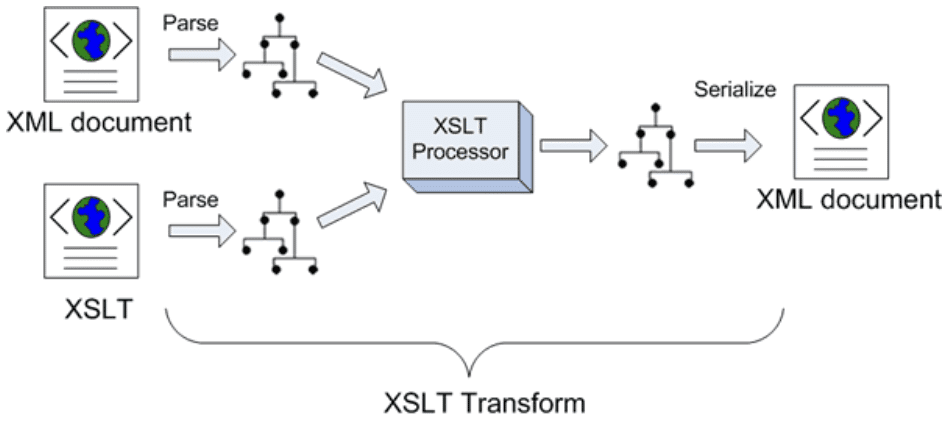
What is XSLT Development?
XSLT developers transform XML using stylesheets—think of it as sculpting data. They take a raw XML dump and turn it into something usable, like a webpage or a report. XPath’s their compass, picking through nodes with precision—a skill that’s easy to botch without practice. In 2025, it’s less trendy, more practical: connecting old systems to new, feeding APIs. Dry, yes, but it keeps data flowing.Role in Contemporary Development
XSLT developers shine where XML persists—web services, legacy stacks, document chains. They’re not just coders; they’re translators. Picture an ancient server spitting XML and a shiny app needing clean output—XSLT bridges that. (I’ve seen projects stall without it—chaos.) By 2025, it’s steady work in niches like healthcare data or tech publishing.Key Competencies
XSLT developers must master:- XSLT and XPath: Version 1.0’s widespread; 2.0’s tougher but potent.
- XML Structure: Schemas, DTDs—the data’s skeleton.
- Scripting: JavaScript or Python often creeps in for heftier tasks.
- Tools: Oxygen XML or Saxon—spot errors before they bite.
They write transforms, test results, ensure data holds up. Detail’s everything here.
Web XSLT Web Pipelines
 XSLT web pipelines turn XML into something browsers can use—HTML, mostly—and JavaScript tags along to liven it up. Developers write XSLT stylesheets to reshape XML, raw stuff from a server maybe, into page-ready chunks. Then JavaScript jumps in—DOM fiddling, like slapping on live updates or form checks. Take an RSS feed: XSLT carves it into a list; JavaScript, running in the browser, tweaks it—grabs extra bits with AJAX, shifts the layout. Been a thing in 2025 for lean web apps—XML’s stiff, but this keeps it breathing.
It’s tricky, though. XSLT does the heavy lifting—XPath digging through nodes—while JavaScript adds the flash. Libraries like jQuery help, save time. (Had a pipeline jam once—handover wasn’t clean.) Needs both to mesh—XSLT’s fixed output fitting JavaScript’s runtime twists. Suits dashboards, aggregators—old XML meeting new tricks, works if you get it right.
XSLT web pipelines turn XML into something browsers can use—HTML, mostly—and JavaScript tags along to liven it up. Developers write XSLT stylesheets to reshape XML, raw stuff from a server maybe, into page-ready chunks. Then JavaScript jumps in—DOM fiddling, like slapping on live updates or form checks. Take an RSS feed: XSLT carves it into a list; JavaScript, running in the browser, tweaks it—grabs extra bits with AJAX, shifts the layout. Been a thing in 2025 for lean web apps—XML’s stiff, but this keeps it breathing.
It’s tricky, though. XSLT does the heavy lifting—XPath digging through nodes—while JavaScript adds the flash. Libraries like jQuery help, save time. (Had a pipeline jam once—handover wasn’t clean.) Needs both to mesh—XSLT’s fixed output fitting JavaScript’s runtime twists. Suits dashboards, aggregators—old XML meeting new tricks, works if you get it right.Why XSLT Developers Matter
XML hangs on—banks, government, tech docs still lean on it. XSLT developers keep that data alive, cutting rework, dodging mistakes. In April 2025, firms with one foot in the past and one in the future need them—badly. It’s not the spotlight; it’s the backbone.Upstaff’s Contribution
Upstaff doesn’t outsource—we’ve got XSLT developers on our roster, built from years of real gigs. They’ve wrestled stylesheets, synced mismatched systems. Looking to hire XSLT developers? We’ve got the know-how—ours—and we pair you with someone who fits. Solo job or team push, we’ve got range. Upstaff.com’s the place—straight to the point.TOP 10 XSLT Related Technologies
XML
XML (eXtensible Markup Language) is a fundamental technology for XSLT software development. It provides a way to structure and store data in a human-readable format, making it easy to exchange information between different systems.XSLT
XSLT (eXtensible Stylesheet Language Transformations) is a powerful language used for transforming XML documents into different formats. It allows developers to define rules and templates to manipulate XML data and generate output in HTML, PDF, or other formats.XPath
XPath is a language used to navigate through XML documents and select specific elements or attributes. It is often used in conjunction with XSLT to define the source data for transformations.XQuery
XQuery is a query language designed for extracting and manipulating data from XML documents. It provides a flexible and expressive syntax for querying XML data, making it an essential tool for XSLT developers.Saxon
Saxon is a popular open-source XSLT and XQuery processor. It provides a robust implementation of the XSLT and XQuery standards and offers advanced features like streaming and parallel processing.Altova XMLSpy
XMLSpy is a comprehensive XML development tool that includes features for editing, validating, and transforming XML documents. It provides a visual XSLT designer and debugger, making it easier to create and test XSLT transformations.Oxygen XML Editor
Oxygen XML Editor is a professional XML development environment that supports XSLT development. It offers features like intelligent content completion, debugging, and profiling tools to streamline the XSLT development process.
How and where is XSLT used?
| Case Name | Case Description |
|---|---|
| Transformation of XML to HTML | XSLT development allows for the transformation of XML data into HTML format. This is particularly useful when working with dynamic websites that require the presentation of XML data in a user-friendly and visually appealing manner. By applying XSLT templates to the XML data, developers can easily generate HTML output that can be rendered by web browsers. |
| Data Integration and Transformation | XSLT development plays a crucial role in data integration and transformation scenarios. It enables developers to map and convert data from one XML schema to another, or even between different data formats such as XML to CSV or XML to JSON. This allows for seamless data interoperability between systems and simplifies the process of data migration and synchronization. |
| Generating Reports | With XSLT development, developers can generate customized reports from XML data. XSLT provides powerful capabilities to extract and transform data, apply formatting rules, and generate printable reports in various formats such as PDF or DOC. This is particularly useful in business applications where generating dynamic reports based on XML data is a common requirement. |
| Web Scraping and Data Extraction | XSLT can be used for web scraping and data extraction tasks. By applying XSLT templates to HTML documents, developers can extract specific data elements and structure the extracted data into XML format. This allows for automated data extraction from websites, enabling tasks such as content aggregation, data mining, or building web-based APIs. |
| Content Syndication | XSLT development facilitates content syndication by transforming and repackaging XML content for distribution across different platforms and systems. By applying XSLT transformations, developers can adapt XML content to meet the requirements of different syndication formats or APIs, ensuring seamless content distribution and integration across multiple channels. |
What are top XSLT instruments and tools?
- Saxon: Saxon is a powerful XSLT and XQuery processor that has been widely used since its initial release in 2000. It is known for its excellent performance and compliance with the XSLT and XQuery standards. Saxon is available in both open-source and commercial editions, offering a range of features and capabilities for transforming XML documents.
- Altova XMLSpy: XMLSpy is an integrated development environment (IDE) specifically designed for XML-related technologies, including XSLT. It offers a comprehensive set of tools for editing, debugging, and transforming XML and XSLT files. XMLSpy has a user-friendly interface and provides advanced features such as XPath auto-completion and XSLT code generation.
- Oxygen XML Editor: Oxygen XML Editor is another popular tool for working with XSLT. It provides a complete set of features for XML development, including powerful XSLT editing and debugging capabilities. Oxygen XML Editor supports XSLT 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0, and offers features like intelligent content completion, XSLT profiling, and integration with version control systems.
- Stylus Studio: Stylus Studio is an integrated development environment that supports XSLT development along with other XML technologies. It offers a visual XSLT designer, which allows users to visually create and modify XSLT stylesheets. Stylus Studio also provides a range of debugging and profiling tools to aid in XSLT development.
- Exselt: Exselt is an open-source XSLT 3.0 processor that aims to provide improved performance and support for the latest XSLT standards. It focuses on optimizing XSLT execution and offers additional features like streaming, schema-awareness, and support for higher-order functions. Exselt is compatible with existing XSLT stylesheets and can be used as a drop-in replacement for other XSLT processors.
- Xalan: Xalan is an open-source XSLT processor developed by the Apache Software Foundation. It has been around since the early 2000s and is widely used in various applications. Xalan supports XSLT 1.0 and provides a Java API for programmatically performing XSLT transformations. Although it may not have the latest features of XSLT 2.0 or 3.0, Xalan remains a reliable and widely adopted XSLT tool.
- BaseX: BaseX is a lightweight and easy-to-use XML database and XQuery processor that also supports XSLT transformations. It provides a graphical user interface for managing XML data and performing XSLT transformations. BaseX is known for its simplicity and efficiency, making it a suitable choice for small to medium-sized projects.
TOP 11 Tech facts and history of creation and versions about XSLT Development
- XSLT (Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations) is a language used for transforming XML documents into various formats.
- It was developed in 1998 by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) and is an integral part of the XML family of standards.
- James Clark, a prominent figure in the development of XML, was the primary author of XSLT.
- XSLT allows for the separation of presentation and content by defining transformation rules using XPath expressions.
- Version 1.0 of XSLT was released in 1999, providing a powerful tool for XML document manipulation and conversion.
- In 2007, XSLT 2.0 was introduced, bringing significant enhancements such as new data types, better support for grouping, and improved error handling.
- XSLT 2.0 also introduced the concept of streaming, enabling the processing of large XML documents without loading the entire document into memory.
- XSLT 3.0, released in 2017, further extended the capabilities of XSLT by introducing support for higher-order functions, improved handling of JSON data, and enhanced streaming capabilities.
- The XSLT development community has created numerous open-source libraries and tools to facilitate XSLT transformations, such as Saxon, Xalan, and Altova XMLSpy.
- XSLT has found wide adoption in various domains, including web development, document processing, and data integration.
- With the rise of alternative technologies like XQuery and JSONPath, XSLT continues to evolve to meet the changing needs of XML transformation and data manipulation.
Talk to Our Expert
Our journey starts with a 30-min discovery call to explore your project challenges, technical needs and team diversity.

Yaroslav Kuntsevych
co-CEO
