Looking to hire Blockchain developer?
At Upstaff you can find industry experts in blockchain:
- hire Crypto Wallet Developer
- hire Web3 Developer
- hire Solidity Developer
- hire Solana Developer
- hire RUST developer
- hire Ethereum Expert
- hire dApp Developer
- hire NFT Marketplace Developer
- hire Smart Contract Audit Specialist
- hire NFT Developer
- hire TG Bots and Mini-Apps Developer
 Are you Looking to build Web3 solutions or transform your business with blockchain tech? At Upstaff.com, we connect you with Blockchain Developers skilled in over 30 blockchain protocols, including Ethereum, Solana, Polygon, and Hyperledger. Our developers are experts in secure smart contracts, decentralized applications (dApps), DeFi platforms, NFT marketplaces, and more. With a rigorous vetting process and flexible hiring options, Upstaff ensures you find the perfect talent to bring your blockchain vision to life. Whether you need a senior developer, a team lead, or a full-stack blockchain engineer, we have that covered.
Hiring through Upstaff.com is effortless and tailored to your needs. Developers, ranging from mid-level to architect-level, have hands-on experience in DeFi protocols, NFT ecosystems, and cross-chain interoperability, cryptography, consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of Work (PoW), and emerging standards like CosmWasm and Substrate.
Are you Looking to build Web3 solutions or transform your business with blockchain tech? At Upstaff.com, we connect you with Blockchain Developers skilled in over 30 blockchain protocols, including Ethereum, Solana, Polygon, and Hyperledger. Our developers are experts in secure smart contracts, decentralized applications (dApps), DeFi platforms, NFT marketplaces, and more. With a rigorous vetting process and flexible hiring options, Upstaff ensures you find the perfect talent to bring your blockchain vision to life. Whether you need a senior developer, a team lead, or a full-stack blockchain engineer, we have that covered.
Hiring through Upstaff.com is effortless and tailored to your needs. Developers, ranging from mid-level to architect-level, have hands-on experience in DeFi protocols, NFT ecosystems, and cross-chain interoperability, cryptography, consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of Work (PoW), and emerging standards like CosmWasm and Substrate.
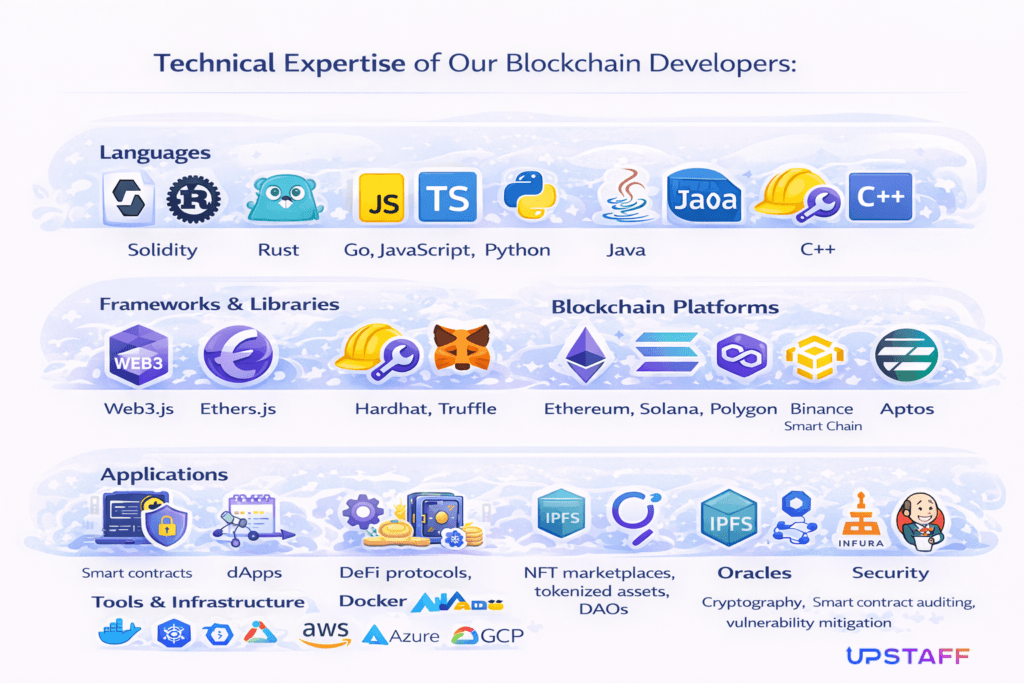 Technical Expertise of Our Blockchain Developers:
Technical Expertise of Our Blockchain Developers:- Languages: Solidity, Rust, Go, JavaScript, TypeScript, Python, Java, C++.
- Frameworks & Libraries: Web3.js, Ethers.js, Hardhat, Truffle, Cosmos SDK, Polkadot Substrate.
- Blockchain Platforms: Ethereum, Solana, Polygon, Binance Smart Chain, Hyperledger, Aptos.
- Applications: Smart contracts, dApps, DeFi protocols, NFT marketplaces, tokenized assets, DAOs.
- Tools & Infrastructure: Docker, Kubernetes, AWS, Azure, GCP, IPFS, The Graph, Oracles (Chainlink, Infura).
- Security: Cryptography, smart contract auditing, vulnerability mitigation.
- Methodologies: Agile, Scrum, Kanban, CI/CD with Jenkins or GitHub Actions.
TOP 12 Facts about Blockchain
- Blockchain is a distributed and decentralized digital ledger that tracks transactions across computers or nodes.
It was originally developed as the basis for the cryptocurrency Bitcoin. - Blockchain works with a peer-to-peer model and does not require banks or clearinghouses
- Any transactions on a blockchain are transparent and can be viewed by anyone on the network.
- Blockchain leverages cryptographic algorithms to ensure that the information on the ledger remains secure and accurate.
- Once a transaction is entered into the blockchain, it cannot be reversed or revoked.
- Blockchain can revolutionize industries like finance, supply chain management, healthcare, etc.
Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts based on predefined rules, can be created on a blockchain and executed to automate tasks. - Blockchain will eliminate fraud and boost trust in a number of industries as it maintains an auditable, foolproof history of transactions.
- Though often associated with cryptos, blockchain has many applications beyond just financial transactions.
- Blockchain networks are either public, open to all, or private, closed only to specific users.
Blockchain can create efficiencies and reduce costs by removing intermediaries and streamlining processes.
TOP 12 Tech facts and history of creation and versions about Blockchain Development
- The blockchain itself was first developed in 2008 by an unnamed individual or collective called Satoshi Nakamoto. It was described in a whitepaper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”.
- Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin use a technology called blockchain. But it’s used in ways that extend beyond cryptocurrency and into other areas like supply chain management, healthcare, voting system, etc.
- Bitcoin, the first blockchain-based product, was introduced in 2009. Bitcoin is a decentralized cryptocurrency that operates on peer-to-peer technology without the presence of a central bank.
- Blockchain is a distributed ledger system where all participants own a copy of the same database, and the database is then refreshed and synced using consensus. This makes blockchain highly secure and tamper-proof.
Another well-known blockchain platform is Ethereum, created in 2015 by Vitalik Buterin. It introduced smart contracts — self-executing contracts in which the contract terms are built into lines of code. Smart contracts enable automated tasks. - By offering transparency, immutability, and greater efficiencies, blockchain technology can transform industries. It can eliminate fraud, remove middle men, and automate difficult workflows.
- “blockchain” refers to the peculiar way that data is grouped into blocks and stacked in a chain. Each block entails a transaction sequence, and each block is cryptographically hashed against the last one.
- Blockchain networks can be public, private or collaborative. Open public blockchains such as Bitcoin and Ethereum allow users to join anonymously. Private blockchains are locked to a specific set of actors, while consortium blockchains are controlled by a set of institutions.
- Blockchain will disrupt the financial industry by making cross-border payments faster and safer, cutting expenses, and providing financial services to the unbanked population.
- Blockchain is now attracting significant attention from governments and international organisations. Some states, such as Estonia, already use blockchain-based e-governance tools and others are exploring how it can be used to manage identities, register land, etc.
- Blockchain is no joke. Scalability, energy usage, regulatory issues, standardization, are just a few challenges that need to be solved before widespread deployment.
- Blockchain has gone beyond the sole purpose of fuelling cryptocurrencies. Now, it is being combined with other technologies such as artificial intelligence, IoT, and big data analytics to create novel solutions.
How and where is Blockchain used?
| Case Name | Case Description |
|---|---|
| Supply Chain Management | Supply Chain Management Blockchain technology can re-engineer supply chain management by enabling visibility, traceability and efficiencies across the entire process. By using blockchain, the company is able to monitor the flow of goods from supplier to consumer, making them authentic and decreasing the probability of fraud or fake goods. The technology also makes everything more efficient by eliminating middlemen, simplifying documentation and automating tasks. |
| Financial Services | Blockchain can revolutionize financial services by increasing security, saving money and speeding up transactions. It supports safe and anonymous peer-to-peer transfers without the need for middlemen such as banks. Blockchain-based cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin provide a substitute for fiat money and also facilitates faster and cheaper cross-border transactions. |
| Healthcare Records Management | Blockchain can solve healthcare records management issues by keeping patient data safe, secure, and interoperable. It gives the patient control over the medical records and allows healthcare providers to have access to the information they need. Blockchain technology also increases data security by eliminating unauthorized access or manipulation of sensitive medical data. |
| Smart Contracts | Blockchain enables the execution of smart contracts, self-executing agreements, with predefined terms and conditions. Such contracts are kept in the blockchain, thus ensuring transparency, irreversibility and contract execution automation. Smart contracts remove the intermediaries and fraud from the equation, thus making business transactions both secure and transparent. |
| Identity Management | Blockchain technology can support identity management processes by enabling safe and decentralized identity authentication. It helps to keep people in control of their online identities, eliminating the possibility of identity theft and fraud. Blockchain identity solutions can reduce steps for KYC (Know Your Customer) verification and provide better, safer customer onboarding across all industries. |
| Voting Systems | Blockchain can improve voting system transparency, security, and integrity. With votes stored on a decentralized, immutable blockchain, voting data cannot be tampered with or altered in the slightest. Voting systems utilizing blockchain can promote voter trust, prevent voter fraud and keep voting records transparent and auditable. |
| Intellectual Property Protection | Protection Blockchain technology can tackle the issue of intellectual property protection by providing creators with a safe and secure environment to register and secure their intellectual property. Blockchain technology enables creations to be timestamped and authenticated, providing evidence of ownership and minimising disputes. Such technology could change the way intellectual property rights are enforced, providing artists with equal compensation. |
Talk to Our Expert
Our journey starts with a 30-min discovery call to explore your project challenges, technical needs and team diversity.

Yaroslav Kuntsevych
co-CEO
