Remote Developer Jobs | Find Top Remote Job Opportunities
The need for remote developer jobs is growing fast in today’s world. With better tools for digital communication and working from a distance, more and more companies are seeing the benefits. They can connect with talented developers no matter where they are. This is changing how work happens worldwide.
More employers want developers who can work from anywhere, not just the office. This trend lets workers find a better balance in their lives. It also lets companies hire from a larger talent pool around the world. So, virtual tech careers are opening up new chances for everyone. Upstaff vs Upwork vs Toptal: Developer Hiring Opportunities Ecosystem Map
Upstaff vs Upwork vs Toptal: Developer Hiring Opportunities Ecosystem Map
With the right mix of technical and soft skills, you can succeed in location-independent coding opportunities. These roles span across many sectors.
Choosing remote coding gigs or distributed development positions depends on what’s important to you. It’s about balancing the good with the not-so-good. This approach helps developers pick what’s right for them and their goals.
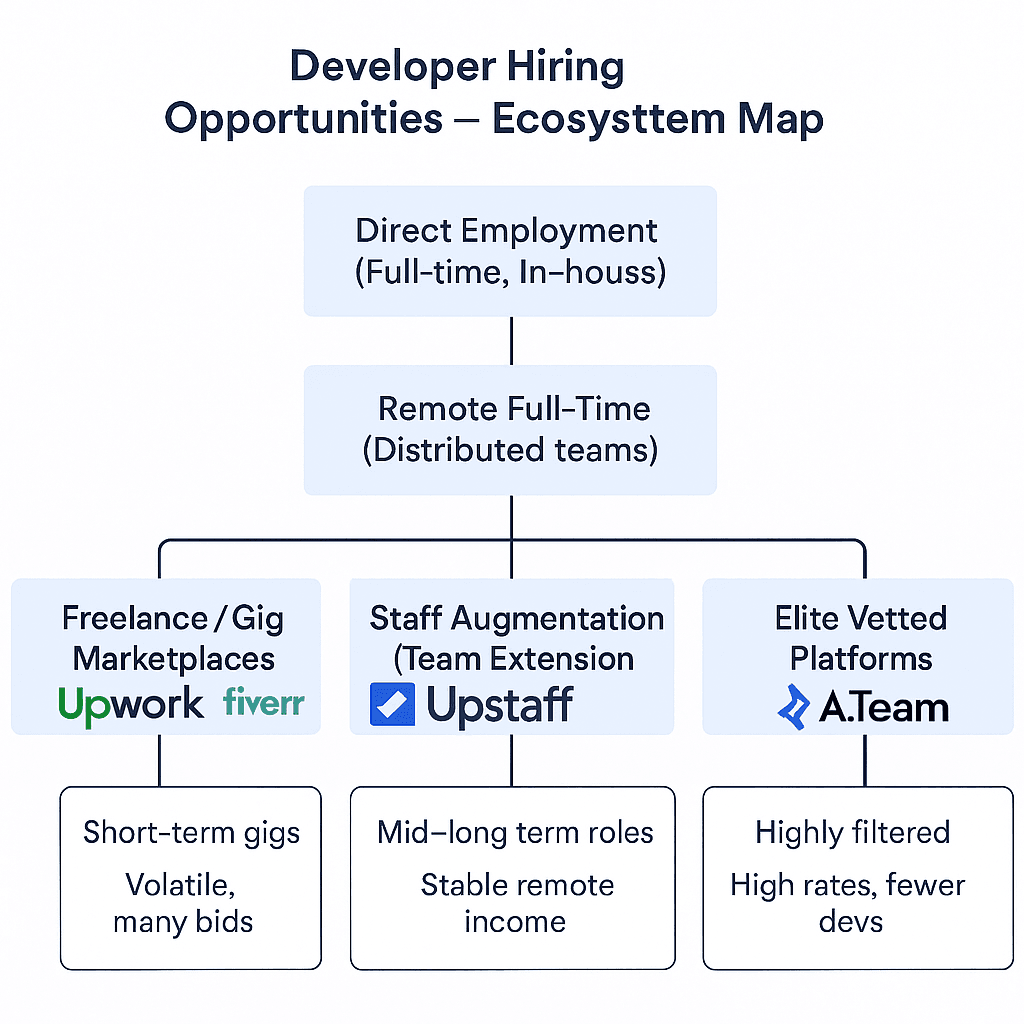 Upstaff vs Upwork vs Toptal: Developer Hiring Opportunities Ecosystem Map
Upstaff vs Upwork vs Toptal: Developer Hiring Opportunities Ecosystem MapWhat kinds of developer hiring opportunities exist now
- Remote and distributed “team-extension” roles: Many companies in EU, US or global tech are hiring developers to join remote teams. These may be full-time/remote, part-time, or contract-based (depending on need).
- Freelance and contract gigs: Short-term or project-based work (ex: build specific features, prototypes, MVPs, one-off tasks in web, backend, AI, blockchain, etc).
- Longer-term and stable remote jobs for mid-senior developers (backend, cloud, AI/ML, blockchain/Web3, data engineering).
- Niche and specialized-skill roles: With the growth of AI, Web3, and data-focused systems. There’s demand for developers with scarce skills (e.g. ML, data-engineering, cloud infra, smart-contract, and blockchain).
- Team-augmentation / staff-augmentation: Especially companies that prefer to outsource or augment their core teams rather than hire full-time in-house. It’s great for companies looking to scale without overhead.
The Rising Demand for Remote Developer Jobs
The job market has changed with the rise of remote work. This change is especially clear in the software development sector. Now, companies are welcoming remote developers, leading to a big increase in demand for their skills.Flexibility and Work-Life Balance
Remote coding jobs are drawing more people because they offer great flexibility and a better work-life balance. No more long commutes! Developers can work from home or anywhere they like. This change allows them to manage their work and personal life better, making them happier and more productive.Global Talent Pool Access
Companies are opening up to borderless IT jobs and digital nomad developer roles. This means they can find skilled developers from all over the world. It helps companies find the best developers for their work, without worrying about where they live. Also, hiring remotely can cut down on costs while maintaining high-quality work. Remote programmer jobs offer more than just saving money and finding the right talent. They help companies build a team of the best developers, no matter where they are. This leads to a workforce that is more diverse and inclusive. Different perspectives and experiences make the team better and stronger.Remote Developer Jobs
The rise of remote developer jobs has changed the game in software development. Now, professionals can work from home or anywhere. This change gives birth to telecommute software engineering roles and virtual tech careers.Types of Remote Developer Roles
There are many kinds of remote developer jobs. You can find work as a:- Web Developers (Front-end, Back-end, and Full-stack)
- Mobile App Developers (iOS and Android)
- Software Engineers
- DevOps Engineers
- Cloud Architects
- Data Scientists
Essential Skills for Remote Developers
For remote developer jobs, you need to be good technically. But, it’s also about having soft skills. Remote work requires a unique set of these skills:| Skill | Description |
|---|---|
| Communication | You need to communicate well, both in writing and talking. This is key for working together and sharing ideas clearly when you’re not in the same place. |
| Self-Discipline | It’s important to keep yourself motivated and on track. Being able to work well alone is a must for remote jobs. |
| Time Management | Good time management helps you stay on top of your work and meet deadlines. This is vital for working from home. |
| Collaboration Tools | Being skilled with online tools like video calls and project apps is crucial for remote team work. These tools help keep everything running smoothly. |
Finding Top Remote Job Opportunities
Today, many professionals want remote developer jobs for flexibility. They enjoy a better work-life balance. It’s key to know where to look for these chances. The right resources and strategies matter a lot. If you’re looking for work from home coding opportunities, plenty of sites can help. Check out Remote.co, WeWorkRemotely, and others. Big names like LinkedIn, Indeed, and Glassdoor also have filters for these jobs. Using them makes job hunting much easier.Networking and Personal Branding
Networking is essential. It can really boost your chances of finding a remote developer job. Go to virtual conferences and join online tech communities. You can also stand out by keeping active on GitHub, LinkedIn, and Twitter. Setting up a portfolio or working on open-source projects can make a big difference. It shows your skills and dedication. This way, you become more visible to potential employers.Pros and Cons of Remote Developer Jobs
Finding telecommute software engineering roles or virtual tech careers can be a big deal for those wanting flexibility and better work-life balance. You get the chance to work from anywhere, end long drives, and have location-independent coding opportunities. This means saving money and being more productive since you can set up your workspace in the best way for you. Yet, remote coding gigs have their own set of issues. Feeling isolated from others, including your team, is a possibility. This may lower teamwork and communication. Excelling in borderless IT jobs requires being really good at managing your time to stay on track and avoid distractions. If you want to live the digital nomad life, untethered programmer openings can be a dream. Working from a café or a beautiful beach sounds amazing. But, it can make separating work from life hard. It’s important to put down clear boundaries and look after yourself.Choosing a digital nomad developer role means considering unique trade-offs. Even though having freedom and flexibility is great, you must think about the challenges.We’ll now go over the main points about remote developer jobs:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Tips for Succeeding in a Remote Developer Role
Taking on a remote developer job or a work from home programming job is thrilling yet challenging. It needs special skills to be successful. If you are experienced or just starting out in telecommute software engineering, these tips will help you do well in your distributed development position. Create a workspace that boosts your ability to focus and work well. Although working from anywhere sounds great, separating work from home life is vital. Think about getting comfy furniture, noise-canceling headphones, and apps to cut down on interruptions. Follow a regular work routine like you would in an office. Use technology to your benefit. Find remote coding gigs that allow for borderless IT jobs and digital nomad developer roles. Try out apps and tools that make it easier to work with others and manage tasks. Good communication is crucial. Keep in touch with your team by sharing updates and asking questions regularly.Talk to Our Expert
Our journey starts with a 30-min discovery call to explore your project challenges, technical needs and team diversity.

Yaroslav Kuntsevych
co-CEO